It has been a remarkable and promising year for medicine, in which a way was found to treat what was now incurable, reversed paralysis and managed to keep the brain alive after death.
“How to step on the moon for the first time”
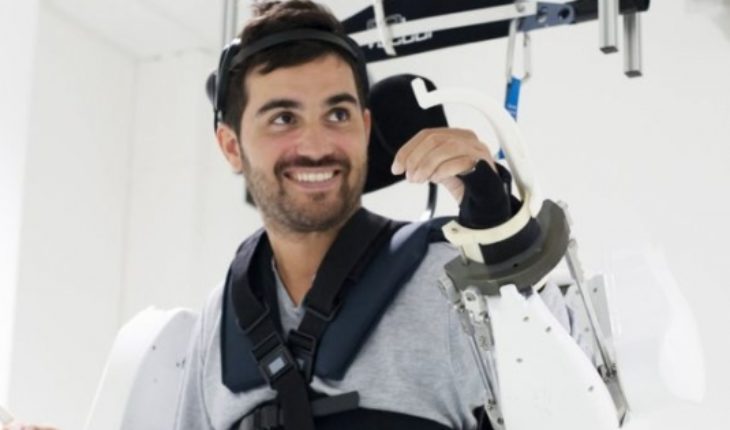
“It was like when man first stepped on the moon,” said Thibault, 30.
The patient was describing the moment he was able to take his first steps since he suffered a paralysis two years ago.
Now you can move your four paralyzed limbs with an exoskeleton that you control with your mind. His movements, particularly walking, are far from perfection and the robotic suit only wears it in the lab.
The innovative exoskeleton who helped a paralyzed man move his four limbs with mental stimuli
But researchers say this achievement will one day improve patients’ quality of life.
In addition, the paralyzed nerves of paralyzed patients managed to be “reconnected” to give mobility to the arms and hands.
As a result, several patients in Australia can now feed themselves, make up, turn a key, handle money and write on a computer.
The revolutionary surgery that returned some of the mobility to paraplegics
A bespoke drug in record time
Experts designed a unique drug for Mila Makovec.Mila Makovec doctors achieved a real feat: designing a unique drug in less than a year to fight their deadly brain disease.
The young girl had been diagnosed with the incurable and deadly disease of Batten, a self-degenerative disorder that causes loss of mental abilities in children with Batten disease.
The team that treated the 8-year-old girl in Boston, United States, produced a complete sequence of her genome and discovered the unique mutation that was causing the disease.
Once the fault was detected, the researchers thought it would be possible to treat it.
Mila Makovec, the girl with a deadly disease who was designed a drug in record time and specifically for her
They then designed a drug, tested on Mila cells and animals in a lab until they got approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Drugs take about a decade to produce and half of them manage to leave the labs and then be tested and then administered to patients.
The American team got all that in a single year.
Now Mila suffers far fewer seizures, although she is not yet cured.
The gene-silencing medicine
Sue Burrell no longer suffers from the heavy bursts of pain before. A new type of drug, known as a “gene silencer,” has shown its effectiveness in reversing previously incurable diseases.
A gene is a part of our DNA that contains the model for producing proteins, such as hormones or enzymes.
But DNA is enclosed inside the nucleus of a cell and separated from the cell’s protein production factories.
Then, our bodies use a short chain of genetic code, called messenger RNA, to close the gap and carry the instructions.
The gene-silencing medicine kills this messenger.
And thanks to him Sue Burrel no longer suffers those outbreaks of severe pain caused by his intermittent acute porphyria.
A virus to the rescue
Isabelle Carnell Holdaway is sipping a cocktail of viruses to fight a dangerous bacteria inside her body. Isabelle Carnell Holdaway’s life was saved by an experimental virus cocktail.
The teenage girl’s body had been attacked by a deadly bacterium that seemed intractable. His chances of survival were less than 1%.
He had dark and suppurant infected areas on his skin.
And he ended up in intensive care when his liver began to fail, while large colonies of bacteria formed in his body.
Phage Therapy: How a Virus Cocktail Saved My Sick Daughter’s Life
But doctors at Great Ormond Street Hospital in London attempted an unproven “phage therapy” until then, which uses viruses to infect and kill bacteria.
Treatment was not conventionally implemented and was soon overshadowed by the discovery of an effective antibiotic for such cases, much easier to use.
But now it’s re-emerging, due to the rise of antibiotic-resistant superbacteria.
So Carnell Holdaway’s case could be the first of many.
An unprecedented way to treat cancer
Charlotte Stevenson was treated with an agnostic tumor drug. Charlotte Stevenson, a 2-year-old girl from Belfast, Northern Ireland, was one of the first patients to benefit from a revolutionary cancer treatment.
They are known as cancer treatments with agnostic indication and the drugs used in them do not care where the tumor develops, as long as it contains a specific genetic abnormality.
The first of these drugs to be developed, the so-called larotrectinib, has already been approved for use throughout Europe.
It is designed to attack tumors with a genetic abnormality known as NTRK gene fusion.
They can be found in Charlotte’s sarcoma, as well as in some types of brain, kidney and thyroid cancers, among others.
And while designing and approving such drugs, immunotherapy reached a major milestone as a cancer treatment.
This therapy uses the patient’s own immune system to fight the disease.
Cancer immunotherapy: what is the revolutionary “living medication” treatment that saved a terminal patient
More than half of melanoma patients, a type of cancer that was considered intractable until just a decade ago, now survive.
What’s more, 10 years ago only one in 20 patients lived up to five years after being diagnosed with late-stage melanoma. Most of them died months later.
The first drug to delay dementia?
A US pharmaceutical company claims to have developed the first drug to slow the development of Alzheimer’s.An US pharmaceutical company claims to have developed the first drug to delay Alzheimer’s disease.
The drug, called aducanumab, is an antibody that removes toxic proteins that accumulate in the brain.
The announcement, made in October, was a big surprise, as the firm Biogen had canceled the drug in March of the same year.
8 of the most inspiring news left by 2019
But then it showed that those who in the experimental tests took the highest doses benefited and better retained memory and language capabilities. Similarly, they performed better in everyday tasks such as cleaning, buying and washing clothes.
If the drug is approved, which is not guaranteed, it would be one of the most important moments in modern medicine.
A new type of dementia
On the other hand, some experts believe they have found a new type of dementia and that in this way millions may have been misdiagnosed.
Dementia is a symptom of many brain diseases and memory loss is the most common feature.
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most common forms of dementia, as are vascular dementia, Parkinson’s disease dementia, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Separate siames
Safa and Marwa were born together in the skull and had never been able to see the faces.
There are no official figures on how often this happens, but it is estimated that every 2.5 million births occur.
The pioneering surgery with which they managed to separate the heads of the Siamese Safa and Marwa
Most people don’t survive more than a day.
Separating these Siamese sisters required multiple surgeries, months of hard work, and the experience of hundreds of hospital workers.
Pig brains “revived” after death
The findings could lead to further advances in treating brain damage. The line between life and death became blurred in 2019.
The brains of pigs were partially revived four hours after the animals were slaughtered.
The study showed that the death of brain cells can stop and that it is possible to reestablish some connections in the brain.
How scientists managed to “resurrect” the brains of several pigs 4 hours after dead
The feat was performed by rhythmically pumping synthetic blood to these organs.
The result challenges the idea that the brain enters into irreversible deterioration within minutes of the blood supply being cut off.
This could lead to new treatments for brain damage and consequential disorders.
Although there were no signs in the “revived” brains indicating consciousness.
Another way to manipulate DNA
The prime editing technique accurately corrects some of the DNA errors. A new way to edit the genetic code could correct 89% of disease-causing DNA errors.
Technology, called prime editing (quality editing”), has been described as a “genetic text processor” capable of accurately rewriting this.
Its operation is similar when copying and pasting word processors.
There are about 75,000 different mutations that can cause disease and researchers say that prime editing can correct almost nine out of 10 of them.
It has already been used to correct harmful mutations in the lab, including those that cause sickle cell anemia and Tay-Sachs disease (a rare and deadly nerve condition).
Give them back their voices those who don’t have it
The electrodes in this implant read brain activity. Scientists have developed a brain implant that can read the mind and turn thoughts into words.
First, an electrode is implanted in the brain to pick up the electrical signals that maneuver the lips, tongue, larynx, and chin.
Then, a powerful computer is used to simulate how these movements in the mouth and throat produce different sounds.
This results in a synthesized speech coming out of a virtual vocal tract.
This system is not yet perfect and not clearly heard, but a team from the University of California, San Francisco says this technology can help people when a disease takes them away from speech.
E-cigarettes that help quit tobacco
50 people have died from diseases linked to the use of e-cigarettes. The vaping has been under intense scrutiny this year.
More than 2,400 people needed hospital treatment, and in the United States, 50 deaths were recorded from “pulmonary injuries associated with the use of e-cigarettes or vaporizers.”
On the other hand, a teenager nearly dies after these devices caused a catastrophic reaction to his lungs.
Electronic cigarette: the “unexplained disease” that caused the first death associated with the use of vaporizers
However, experts insist that the vaping it’s safer than smoking tobacco, and this year they’ve provided evidence that it helps smokers stop.
The essay, published in the journal New England Journal of Medicine, found that 18% of smokers who used it did not smoke again after a year, compared to 9.9% using traditional nicotine replacements.
Other events that caught our attention:
Researchers captured unprecedented images of a baby’s heart inside the uterus.
Measles has devastating effects on the immune system, leaving it weakened to fight other infections for years.
The origins of anorexia are found in the mind and body, with changes in some people’s DNA that alter the way they process sugars and fats.
A diet rich in bananas, chickpeas and peanuts can activate good gut bacteria that help children with malnutrition grow.
The body continues to produce cells until age 97.
A fungus, genetically enhanced to produce spider toxin, can quickly kill large amounts of malaria-transmitting mosquitoes.
It may not be a surprise, but what we eat puts 11 million people at risk of premature death.
Scientists have disarmed cancer in parts to reveal its weaknesses, and propose new ideas for treatment.
translated from Spanish: The revolutionary medical advances of 2019 (and those you may not have known about)
December 31, 2019 |