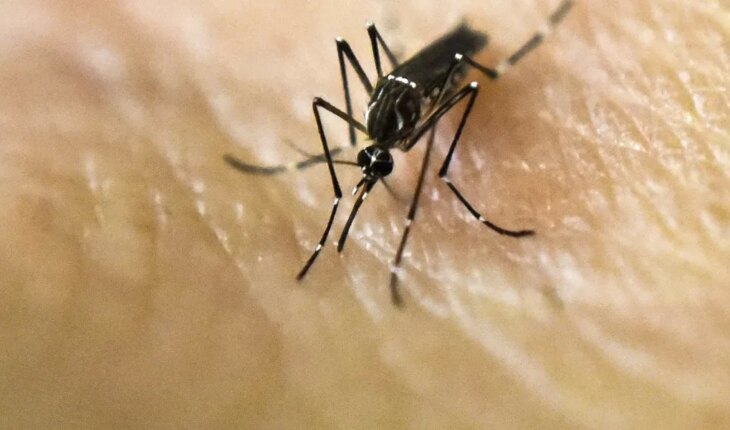
The Ministry of Health of the Nation reported that until epidemiological week 16, that is, until 23/04, 71,717 cases of dengue were reported, of which 65,195 acquired the infection in Argentina. So far, mosquito circulation has been identified in 16 jurisdictions corresponding to four regions: Central Region (Buenos Aires; Autonomous City of Buenos Aires -C.A.B.A.-; Córdoba; Entre Ríos; Santa Fe); NEA region (Corrientes; Formosa; Chaco), NOA region (Catamarca; Jujuy; La Rioja; Salta; Santiago del Estero; Tucumán) and Cuyo Region (San Luis and Mendoza). When observing the curve of cases, the Ministry reports that there was “a sustained progressive increase between epidemiological week 5 and 13 (January 29 to March 31), after which a decrease is verified, that is, in weeks 14 and 15 (April 2 to 15) there is a lower number of cases, a 31% and 23% decrease respectively, always in relation to the peak”. This drop in cases is occurring in jurisdictions such as Tucumán; Santiago del Estero; Salta; Jujuy; Autonomous City of Buenos Aires and Buenos Aires. In turn, Health recommends reinforcing care against temperature increases these days. With regard to chikungunya fever, 1,460 cases have been registered so far, of which 910 have acquired the infection in the country; while another 260 suspicious pictures are under investigation. Dengue is a viral disease transmitted by the bite of the mosquito of the genus Aedes, mainly by Aedes aegypti. When the mosquito feeds on blood from a person infected with the dengue virus, it acquires it and after 8 to 12 days it is able to transmit it to a healthy person through the bite. Mother-to-child transmission is possible but rare. Chikungunya fever is also a viral disease that, like the one mentioned above, is transmitted by the bite of infected Aedes mosquitoes and can also be transmitted from mother to child in the perinatal period.
Dengue: a decrease in cases for the second consecutive week
April 30, 2023 |