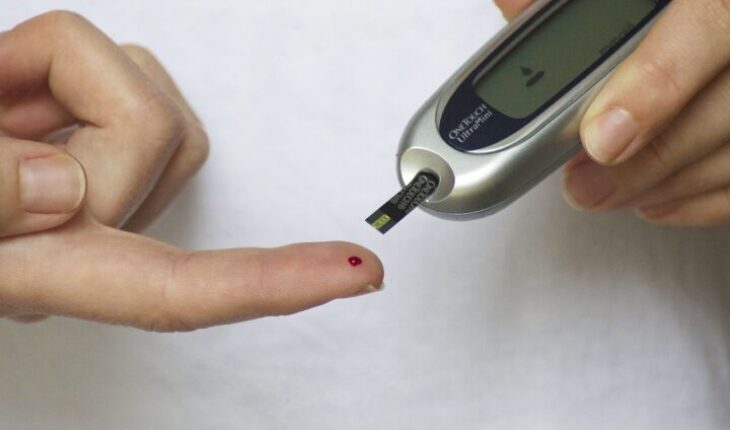
World. – It is essential to be aware of our body’s capabilities and restrictions in order to identify potential problems that need medical attention or laboratory tests. In addition to monitoring vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and breathing rate, it is crucial to also know our glucose levels to prevent metabolic diseases, such as diabetes, and their potential complications. You’ve probably wondered on several occasions what the normal blood glucose level is and how it can be measured. To avoid possible confusion, it is necessary to clarify that glucose is a type of sugar present in the blood, and is the main source of energy for our body. It originates from the food we eat and is transported through the bloodstream to all cells, where it is used as fuel. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, facilitates the entry of glucose into cells for energy use. Glucose plays other vital roles, such as being a structural component in plant cellulose and participating in the storage of energy in the form of glycogen in the liver and muscles. Maintaining a proper balance of glucose in the body is essential, as high or low levels can lead to health problems, such as diabetes. Blood glucose levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Values considered normal for fasting blood glucose for adults are:Less than 99 mg/dL: Normal100 to 125 mg/dL: Prediabetes126 mg/dL or more: DiabetesIt is also possible to measure blood glucose levels after meals. Values considered normal for postprandial blood glucose are:Less than 140 mg/dL: Normal140 to 199 mg/dL: Prediabetes200 mg/dL or more: DiabetesUnusual blood glucose levels may signal the presence of a medical condition, such as diabetes, prediabetes, or hypoglycemiaDiabetes. It is a chronic condition that alters the way the body metabolizes glucose, which is a form of sugar and the body’s main source of energy. In individuals with diabetes, the body cannot use glucose effectively, which can result in elevated blood glucose levels. Type 1 diabetes: This is an autoimmune disease that causes the destruction of beta cells in the pancreas, which are responsible for the production of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that makes it easier for the body to use glucose. Type 2 diabetes: This variant is the most prevalent form of diabetes and results from the interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Prediabetes. It is a situation that occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal, although they do not reach the threshold to be diagnosed as diabetes. Those with prediabetes face an increased risk of developing diabetes. Hypoglycemia. It is defined as a condition that occurs when blood glucose levels are too low. Hypoglycemia can be caused by a variety of factors, such as diabetes, the use of certain medications, or prolonged fasting. Symptoms of hypoglycemia can include sweating, shaking, lack of concentration, dizziness, anxiety, confusion, and loss of consciousness. It is worth mentioning that in case you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to eat food or consume fruit juice to raise blood glucose levels.
Original source in Spanish
What are normal glucose levels? – MonitorExpresso.com
February 13, 2024 |